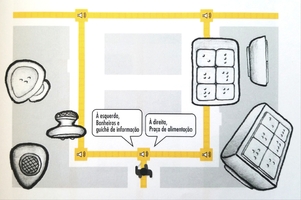
Assistente: uma proposta de sinalização para pessoas com deficiência visual
Para um design atuar em um projeto onde a visão não é o sentido primário, onde as cores, tipografia ou diagramação não existem, é um grande desafio. Por isso, observando um déficit de trabalhos brasileiros na área do design que abordam deficiência visual, o projeto visa uma releitura do sistema de sinalização que utiliza o piso e o mapa tátil voltado para pessoas com deficiência total e parcial da visão, a partir de pesquisa com os alunos do Instituto Benjamin Constante. O ASSISTENTE combina tecnologia RFID com o piso tátil, fazendo com que mensagens sonoras associadas a trechos do piso auxiliem na locomoção da pessoas com deficiência visual em locais fechados, garantindo maior autonomia na deslocação. As Tags passivas RFID são aplicadas sob o piso emborrachado e emitem a informação ao aparelho receptor carregado pelo deficiente visual quando entra no raio de leitura, produzindo, então, uma mensagem por um fone sem fio.
For a design to act in a project where vision is not the primary sense, where colors, typography or layout do not exist, is a great challenge. Therefore, observing a deficit of Brazilian works in the design area that address visual impairment, the project aims at a re-reading of the signaling system that uses the tactile floor and map aimed at people with total and partial visual impairment, from research with students from the Benjamin Constante Institute. ASSISTENTE combines RFID technology with the tactile floor, making it so that sound messages associated to passages on the floor assist the locomotion of people with visual impairment in closed places, ensuring greater autonomy in their movement. The passive RFID tags are applied under the rubberized floor and emit the information to the receiving device carried by the visually impaired when they enter the reading range, and then produce a message through a wireless headset.